ENTREPRENEURIAL OPPORTUNITIES IN URBAN PLANNING PROFESSION
LESSON 1: ENTREPRENEURIAL PROCESS AND OPPORTUNITIES
1.1 Introduction
Entrepreneurship has taken a prominent place in economic and general job creation in recent discussions, some of these are backed with facts while some others are mainly guesswork. Nevertheless, entrepreneurship is clearly an essential component and driver of national development stimulating employment generation across different strata of the society. Entrepreneurship holds so many benefits for the people, it enables opportunities to solve challenging social, economic, development, cultural and technological problems. However, there is a need to master the process of entrepreneurship, this enables easy identification of opportunities, address the issue of entrepreneurial financing; enhance the process of business setup and enable prospective or practicing entrepreneurs to derive maximum benefits from the process.
This 5-day email workshop focuses on these areas of entrepreneurship, the topics that would be covered in this five-day email workshop are entrepreneurial process and opportunities; urban planning profession entrepreneurial opportunities; entrepreneurial opportunities execution tools; execution of urban planning entrepreneurial opportunities and case studies of planning entrepreneurial opportunities. In this lesson one, I am going to focus on entrepreneurial process and opportunities, the lesion is divided into seven parts, these are: introduction; understanding entrepreneurship; generating entrepreneurial insights; lean entrepreneurship idea; entrepreneurial finance; entrepreneurial challenges and factors; and entrepreneurial opportunities overview
1.2 Understanding Entrepreneurship
Tom Eisenmann said an “entrepreneurs must create and deliver something new—a solution to a customer’s problem that’s better than, or costs less than, current options.”. I like this definition because the focus is on what is offered rather than the age or size of the venture. Hence an entrepreneur should CREATE and OFFER VALUE. As an entrepreneur, what issue do you want to address? What solutions do you have to offer? What are the customers’ pain points you want to alleviate? This I believe is how we should see entrepreneurs and entrepreneurship.
In entrepreneurship, there are inherent risks, the immediate future is not totally foreseeable, though we engage in different projections and calculations, however, there is some degree of probability. Some of the risks in entrepreneurship include demand risk; technological risk; execution risk; and financing risk. These are hazards that need to be planned, it needs to be overcome so as not to derail the entrepreneurial journey.
Entrepreneurship is a way of thinking, reasoning, and acting with intense focused on solutions activities ultimately towards capturing value for the entrepreneurs and the general society. Entrepreneurship should not be about the blank firing, aimless shots or efforts, there are procedures and processes to entrepreneurship. The entrepreneurial mindset is the belief system, the thought process and behavioural pattern. There are different versions of what the mindset of an entrepreneur should be, however, across all these versions there is some form of agreement, from my conclusion an entrepreneur should be positive-minded, curious, have the basic numeral ability; creative with good verbal and non-verbal communication skills. Tenacity is also one of the desired mindsets, however flexibility is also required, the ability to change position regardless of how tenacious one is. These mindsets could be developed by setting clear goals and by also sticking to the goals; however, these goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, realistic with time a well-defined time frame. The entrepreneurship process entails a stream of activities that are needed to actualize an entrepreneurial idea - this starts from problem/issue identification, idea conception, team selection, resource identification, identifying customer pain points, market testing, financing, prototype to services/product launch. It should be noted that this is not necessarily a linear process, sometimes these steps could be alternated.
1.3 Generating Entrepreneurial Insights
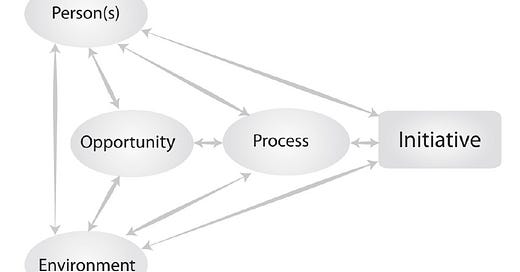
Entrepreneurship is mostly about seeing and seizing opportunities. This revolves around addressing challenges and issue to create and offer value for benefits, these benefits could be financial, social and moral benefits to the entrepreneurs. Identifying opportunities has to do with judgement and decision process – how do we identify opportunities? What do we look out for? In generating entrepreneurial ideas for business setup there are important components. These components as identified by Nils Nilsson are the persons (entrepreneurs); environment; opportunity; process and initiatives (the entrepreneurial idea) Figure 1.
These components (persons; environment; opportunity; process) has to work together as a system, all the components are important, needed to interact smoothly to generate good initiatives (entrepreneurial ideas). The four items (persons; environment; opportunity; process) are inputs resulting in an output - initiative (the entrepreneurial idea). Nils aptly capture these components this way “the person(s) enters into an environment, where they eventually notice an opportunity; they then engage in an entrepreneurial process to develop and form a ‘response’, which, if the process is successful, results in a new, value-generating initiative.”. The person(s) dimension focuses on character, education, what need to learn; for the environment, the focus is on should we explore the existing environment or create; with regards to the opportunity, what are people pain points, what do they people lack, what are their desires and what plan are needed to actualize the entrepreneurial idea(s).
Figure1: Entrepreneurial Idea Generation Components
Source: Nils Nilsson, The Entrepreneurial Process, 2021
1.4 Lean Entrepreneurship Idea
Entrepreneurship could be taken as part science and art; it involves some level of methodical practice and similarly there is also some form of randomness. However, the intuitive dimension should never be blown out of proportion to avoid the glamorizing of entrepreneurial activities. Lean entrepreneurship idea is about starting out at a minimal level, it enables entrepreneurs to test the market, understand the pulse of the market and therefore enables the entrepreneurs to fine-tune the services or product to the consumer’s desires. The ultimate aim is to reduce the level of waste that could result from false entrepreneurial start. The central idea of lean entrepreneurship is agility and continuously learning. Basically, as an entrepreneurial urban planner develop what is regarded as minimum viable product (MVP) either services or products, take it to the market, learn what the market says, and refine to fit the consumer’s desire.
Steve Blank and Eric Ries pioneered the idea of ‘Lean Startup’, central to the Eric Ries lean startup idea is the ‘Build-Measure-Learn” framework (Figure 2), a feedback loop. The build stage involves identifying problem/issue that requires a solution, building a minimum viable product, a minimal version of your urban planning product or service, for example, if you decided to engage in a digital mapping system, you could develop a basic version of this without huge capital outlay required for a full version, take to this market, presents to the prospective users to understand their perception and the performance of the product/service. Measure the outcome of the results from the exposure of your urban planning products/services using the right metrics (measurement parameters) and learn from the experience, the results and decide either to continue or discontinue with the idea.
Source: www.1mproves.com
1.5 Entrepreneurial Finance
Entrepreneurial finance revolves around how to address the issues of financial management in your entrepreneurial journey, this is one of the major challenges of entrepreneurs and need to be taken on early in your urban planning entrepreneurial journey. How do you source capital for the startup? Is there any issue of debt to be address? How do you manage the business cash-flow? What organize your financial statements? What is your plan on marketing and sales of products and services? What do you do with the startup valuation? Are you building to sell? All these questions are imperative entrepreneurial finance questions that need to be thoroughly and objectively answered. As an urban planner interested in an entrepreneurial journey you need to have a basic understanding of these entrepreneurial financial issues. However, it is not compulsory that you have advanced level of knowledge of these issues, you could engage the services of qualified professionals to carry out these tasks for you.
1.6 Entrepreneurial Failure and Factors
Tom Eisenmann the revered entrepreneurship and new ventures professor at Harvard Business School wrote a book in 2021 titled “why startup fail”, he identified six major reasons why the majority of entrepreneurial ventures fails, these reasons have global applications, that is, it could be seen as reasons for entrepreneurial ventures failure across different countries. These include dysfunctional relationships between the parties involved in the entrepreneurial idea - relationships among the founders, employees, investors and other partners. Another reason for entrepreneurial venture failure is the lack of market for the idea most of the entrepreneurs fails to understand the markets and customers need. Also; excessive optimism on the entrepreneurial idea with regards to market demand, source of finance etc. often causes the idea to fail.
Furthermore, growing too fast and poor external advice could cause an entrepreneurial venture to fail. Other factors by other business thinkers include poor business model; poor change management; poor assessment of competitors; poor locational decision for the business; funding challenges; poor customer service; poor market assessment. CB Insights highlighted twelve reasons for entrepreneurial ventures failures (See Figure 3). Similarly, the entrepreneurial landscape in Nigeria is replete with myriads of challenges with regard to finance, policy issues and inadequate support framework for small and medium scale enterprises.
Please note that the focus of this section of the workshop is not scare would-be entrepreneurs and deter them, but to give a form of EARLY WARNING SYSTEM FRAMEWORK, these are likely challenges you could face in your entrepreneurial journey, watch out for these factors and plan ahead for them. In the course of thinking about your entrepreneurial ideas, you should also be thinking about how do I avoid or work around these failure factors. So, I implore you to take the above-mentioned entrepreneurial failure factors as EARLY WARNING SIGNS to enhance the success of your entrepreneurial exploration.
Source: cbinsights.com/research/startup-failure-reasons-top
1.7 Urban Planning Entrepreneurial Opportunities Overview
The next lesson (lesson two) would focus on different entrepreneurial opportunities available to prospective, young urban planners and practicing urban planner, the opportunities exploration would focus on the traditional and digital planning sphere. The discussion would highlight the opportunities WHY and WHAT, why the opportunities and what to do with practical Nigeria and global illustrations